An engineer’s diary
-
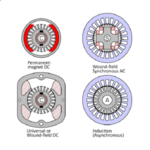
[No. 17] Classification of electric machines
The diagram shows most of the electric machines in common use, together with the two reluctance machines which are rare but interesting. Classification is much more than an acade…
-

[No. 18] Is it time to celebrate?
In Finite Elements in Electrical and Magnetic Field Problems, edited by M.V.K. Chari and P.P. Silvester, (Wiley, 1980, ISBN 0 471 27578 6), A.L. Frisiani, G. Molinari and A. Vivia…
-
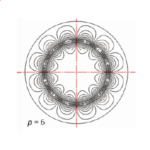
[No. 19] The number of poles in a rotary electrical machine
The figure shows the some of the effects of pole-number on the magnetic field in a rotary electrical machine. It is a highly idealised figure: the winding is a current-sheet in th…
-
[No. 20] Equipotentials
Sometimes I wonder why we don’t see equipotentials in finite-element flux-plots. Strictly speaking, at least in 2D flux-plots, we generally do see them because the flux-lines…
-
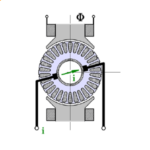
[No. 21] What is a space-vector?
A space-vector — let us say, a space-vector of current — is a single complex number representing the combined effect of all three phase currents in an AC machine at a particular i…
-

[No. 22] What can we do when we can’t go to work?
Many engineers are at home because of the pandemic, unable to go to work. Although many can work “from home” by internet links, it’s not the same.
-
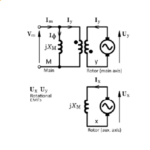
[No. 23] The complexity of the single-phase induction motor in your refrigerator
The single-phase induction motor is one of the most common electric motors. For many years the annual production levels world-wide have been 100,000,000 in round numbers. You can …
-
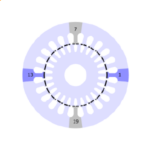
[No. 24] Synchronous torques in induction motors
Fig. 1 shows two types of irregularity in the speed/torque characteristic of an induction motor — the asynchronous torque dip and the synchronous torque dip. These are sometimes c…
-
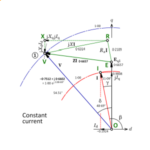
[No. 25] Constructing and reading the flux-weakening phasor diagram
This article concerns the permanent-magnet brushless AC motor. We’re going to review the phasor diagram, which has been the basis of AC motor theory for about 120 years. We will c…
-
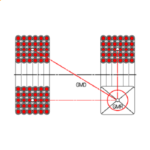
[No. 26] The remarkable work of Rosa and Grover
One of my teachers (Dr. Thomas Foord) gave undergraduate lectures that were so clear, I feel as though I could repeat them nearly 55 years later. Of course I could not do it. That…
-
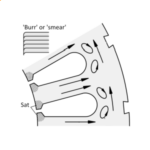
[No. 27] Loss Segregation
Like many quotations, this is a shocking example of quoting someone out of context. It comes from Cyril G. Veinott, writing in 1935, [1].That sentence is followed by seven others …
-
[No. 28] Notional equations in engineering
On the telephone recently my 8-year-old grandson asked if I knew the equation E = mc^2. When I said I’d heard of it, he proceeded to explain: E is energy, m is mass, and c is the …
-
[No. 29] Theory and practice in engineering training
The training and education of engineers is hurt by the pandemic and the associated restrictions imposed everywhere We hear of the difficulties experienced by schools and colleges,…
-

[No. 30] Rotational EMF
In electrical machine theory we often hear the term rotational EMF. What exactly does it mean?“EMF” means “electro-motive force”. In electrical machine theory it is a voltage indu…
-
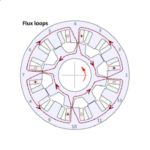
[No. 31] Some essential features of the switched reluctance motor
Every type of electric motor has certain essential features. One way to begin to understand them is to make a drawing, and at the same time make a list of observed features and ch…
-
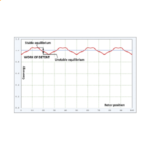
[No. 32] Work of detent
Torque ripple is the variation in the torque of an electric machine as the rotor rotates. It depends on many factors including the current waveform, but in permanent-magnet motors…