*Please prepare a license ID and password for the license administrator.
*It is different from the service for JMAG WEB MEMBER (free membership). Please be careful.
Overview

Deformation occurs when large metal parts such as shafts undergo machining, causing their material properties to worsen. Because of this, these material properties are restored by eliminating machining deformations using thermal processing, which returns the metal structure to its standard condition. It is necessary to heat the whole part to the same temperature in order to restore the metal’s overall properties with thermal heating, and ohmic heating is often used for this purpose. It is helpful to measure the temperature distribution in advance with an investigation of heating conditions.
Evaluation with analysis based on the finite element method (FEM) is necessary to find whether a product with a 3D geometry is heated uniformly by a given electrode configuration.
This Application Note presents how to obtain the temperature distribution, temperature variations, and heat flux distribution in a body heated by ohmic heating.
Evaluation with analysis based on the finite element method (FEM) is necessary to find whether a product with a 3D geometry is heated uniformly by a given electrode configuration.
This Application Note presents how to obtain the temperature distribution, temperature variations, and heat flux distribution in a body heated by ohmic heating.
Temperature Distribution
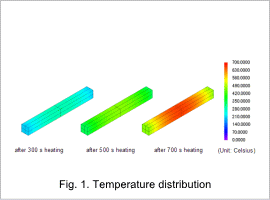
The temperature distribution of the heated body is shown in fig. 1. From the figure, it is apparent that the central portion of the heated body has the highest temperature at all times.
Temperature Variations
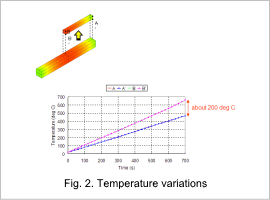
Temperature variations at each measurement point A, A’, B, B’ are shown in fig. 2. In the figure, it can be seen that there is no temperature variation between the surface and the inside (A-A’, B-B’).
Also, there is a temperature variation between the ends and the central portion (A-B, A’-B’) as seen in fig. 1, and this temperature variation is 200 deg C after 700 s of heating.
Also, there is a temperature variation between the ends and the central portion (A-B, A’-B’) as seen in fig. 1, and this temperature variation is 200 deg C after 700 s of heating.
Heat Flux Distribution
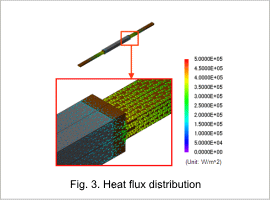
The heat flux distribution at 700 s is shown in fig. 3. From the figure, it is clear that heat is conducted from the heated body to the electrodes, and that this is the cause of the temperature variation along the lengthwise direction of the heated body.
Some means of reducing this temperature variation in the lengthwise direction is necessary in order to uniformly heat the body and improve its properties.
Some means of reducing this temperature variation in the lengthwise direction is necessary in order to uniformly heat the body and improve its properties.