Overview
Design automation has been highlighted as a key toward evolving the development process of electric machines. Optimizations that automatically analyze dimensions and other specifications that can satisfy the machine requirements are drastically advancing design automation. However, optimizations that run genetic algorithms (GA) require a significant number of finite element analyses (FEA). These simulations can take anywhere from several hours to multiple days even when using distributed or parallel computing. More and more optimizations require the use of three-dimensional models, but this creates a bottle neck due to the time required to run them. Offline optimizations are one approach to address this fundamental challenge to design automation.
Offline optimizations explore Pareto solutions quickly by utilizing surrogate models created in advance in place of FEA. Optimizations can run analyses over and over in a short time because no new FEA are necessary. Offline optimizations are advantageous during the initial design stage when narrowing down the type of motor and changing design requirements.
This case study runs an offline optimization to explore the optimal geometry for an axial gap motor to maximize average torque and minimize losses. A constraint condition anticipates the inverter voltage will change from 120 volts to 100 volts. The use of a surrogate model reduces the time required for the optimization to about 1/25th that of one using only FEA.
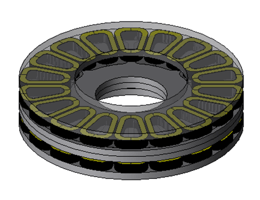
Axial Gap Motor
Optimization Requirements
| Design variables | Frame width, inner/outer diamter of magnets, flatness ratio, and current amplitude/phase |
| Constraint conditions |
Voltage change: 120 (V) or less to 100 (V) |
| Objective functions | Maximize average torque/ minimize losses |
Fig. 1 Axial Gap Motor and Optimization Requirements
This case study runs a parametric optimization of an axial gap motor. As outlined in the table on the right, the constraint condition changes the inverter voltage from 120 volts to 100 volts.
You need to sign in as a Regular JMAG Software User (paid user) or JMAG WEB MEMBER (free membership).
By registering as a JMAG WEB MEMBER, you can browse technical materials and other member-only contents for free.
If you are not registered, click the “Create an Account” button.
Create an Account Sign in