Contents
1. Introduction
2. Time-Periodic Finite Element (TP-FEM) Method and Time-Periodic Explicit Error Correction (TP-EEC) Method
3. Important Assumptions to Know
4. Conclusion
5. References
1. Introduction
In electrical equipment design, Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) software is used to make the best possible products within allowable timelines. In particular, finite element analysis (FEA) for the electromagnetic field is often used because of its true expressiveness of the geometries and easy handling of the nonlinear characteristics of materials. JMAG is one of the electromagnetic field FEA software, and we realize that reduction of processing time is in great demand from our software users. In order to achieve this reduction, JMAG has been improved the nonlinear iterative solver and ICCG solving method as well as updating shared memory and distributed memory type parallel processing for the effective use of many cores.
On the other hand, in case of the model with a large time constants in eddy current analysis, there is the problem that many time steps are required to obtain a steady state. To counteract this, the time-period finite element method (TP-FEM method) is proposed. With this method, the steady state can be directly solved without having to go through the transient state. Furthermore, the dimension of simultaneous linear equations to be solved are the product of unknowns per time step and the number of time steps of one period or half period, which has a drawback in calculation cost. To overcome this challenge, the time periodic correction method (TP-EEC method) has been proposed in recent years. In that method, by applying the Explicit Error Correction method (EEC method) with the TP-FEM method as its base, error components with slow convergence times are removed.
As there have been many previous investigations on the effectiveness and performance of generic TP-EEC methods, please take a look at those for further reference. In this report, we will briefly cover specific processes of the TP-EEC method adopted by JMAG, and show the situations in which the TP-EEC method is weak, and also the situations in which its use is powerful.
The intent of this material is to inform its readers, and to help them to decide the applicableness of these methods to their own models.
2. Time-Periodic Finite Element (TP-FEM) Method and Time-Periodic Explicit Error Correction (TP-EEC) Method
As mentioned above, the TP-EEC method is based on the TP-FEM method. Therefore, in this section, the TP-FEM method will be explained 1st. In this method, the following equations are solved to obtain results at N time steps corresponding to one period or half period at once.
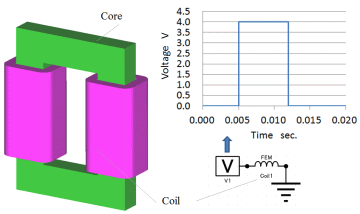
Reactor model
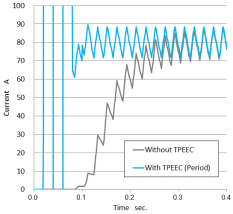
Current history when periodic TP-EEC method is applied
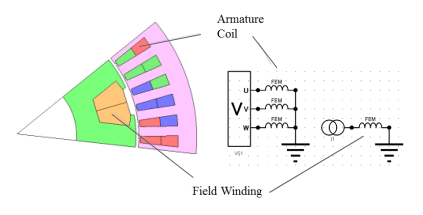
Synchronous rotating machine model
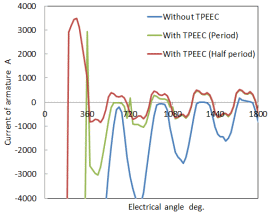
Armature coil winding current history
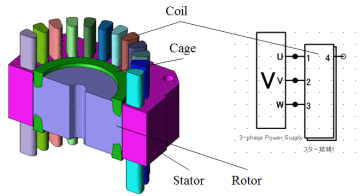
Induction machine model
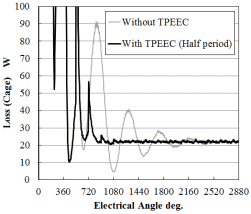
Torque history (slip 0.1)
You need to sign in as a Regular JMAG Software User (paid user) or JMAG WEB MEMBER (free membership).
By registering as a JMAG WEB MEMBER, you can browse technical materials and other member-only contents for free.
If you are not registered, click the “Create an Account” button.
Create an Account Sign in