Overview
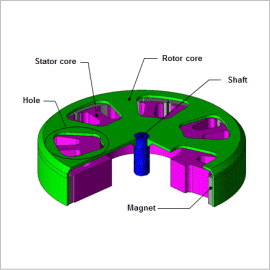
The electromotive force is a cause of the vibration that occurs when a motor rotates. Additionally, when this electromotive force resonates with the motor’s eigenmodes, it causes even larger vibrations and noise. Countermeasures such as changing the motor’s eigenfrequency through processes like setting a hole in the rotor core have been taken with the objective of preventing resonance. In order to carry out these kinds of studies, it is necessary to get a precise, definite grasp of the electromotive force’s spatial distribution, frequency analysis, and natural frequency.
This note presents the use of a magnetic field analysis and structural analysis to obtain the sound pressure caused by electromagnetic vibrations in an outer rotor motor with holes fabricated in the rotor core.
Electromagnetic Force Distribution
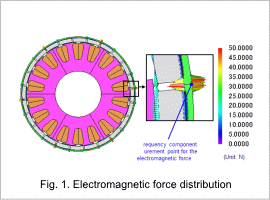
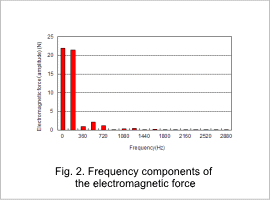
Fig. 1 shows the electromagnetic force distribution where the electromagnetic force is greatest among the frequency measurement component points, and Fig. 2 shows the frequency components of the electromagnetic force displayed at the points in Fig. 1. The frequency components of the electromagnetic force are concentrated at 180 Hz and the electromagnetic force is larger between the rotor core and poles.
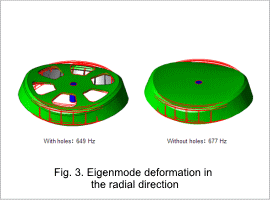
Eigenmode
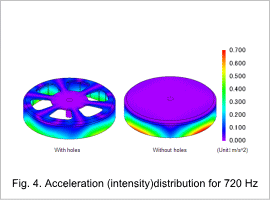
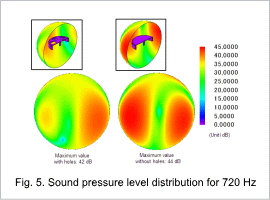
Acceleration (Intensity) Distribution and Sound Pressure Level Distribution
The acceleration (R-RMS) distribution at 720 Hz is indicated in Fig. 4.4 and the sound pressure level distribution at 720 Hz is indicated in Fig. 4.5. The electromagnetic force takes effect, and it is possible to confirm a large acceleration and a high sound pressure level distribution due to the resonance phenomenon at an eigenfrequency of 720 Hz, a frequency close to the eigenfrequency shown in 4.2 “Eigenmode”. Fig. 4.4 and Fig. 4.5 show that opening holes shown below can suppress acceleration in the R direction and reduce noise in this motor.