*Please prepare a license ID and password for the license administrator.
*It is different from the service for JMAG WEB MEMBER (free membership). Please be careful.
Overview
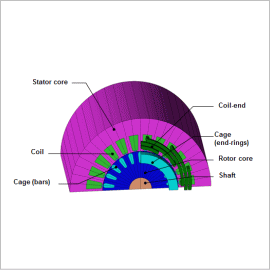
An induction motor is a motor in which the rotating magnetic field of the stator winding causes induced current to flow in an secondary conductor, which exerts force on the rotor in the rotational direction and causes it to spin.
In an induction motor, magnetic flux in the axis direction, such as leakage flux in the coil end, can have a large effect on motor characteristics. However, transient phenomena are strong in the inductance motor, and analysis time is needed in order to achieve a steady state solution. Due to this, being able to evaluate characteristics in a 2D analysis is desirable, but 3D effects such as leakage flux in the coil ends are ignored in a 2D analysis, and there are cases when an accurate analysis cannot be obtained. In JMAG, highly accurate results can be quickly obtained by performing corrections on 3D effects.
This document introduces introduces a case study which obtains inductance correction values, and then obtains N-T characteristics (revolution speed-torque characteristics) using the 3D correction function.
In an induction motor, magnetic flux in the axis direction, such as leakage flux in the coil end, can have a large effect on motor characteristics. However, transient phenomena are strong in the inductance motor, and analysis time is needed in order to achieve a steady state solution. Due to this, being able to evaluate characteristics in a 2D analysis is desirable, but 3D effects such as leakage flux in the coil ends are ignored in a 2D analysis, and there are cases when an accurate analysis cannot be obtained. In JMAG, highly accurate results can be quickly obtained by performing corrections on 3D effects.
This document introduces introduces a case study which obtains inductance correction values, and then obtains N-T characteristics (revolution speed-torque characteristics) using the 3D correction function.
Self Inductance
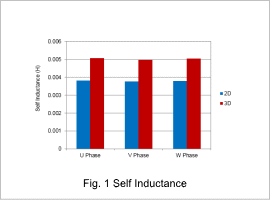
Fig.1 shows the results of self inductance at lock tests.
Fig.1 shows that inductance has decreased by approximately 25% in a 2D analysis when compared to a 3D analysis. This is because a 2D analysis cannot account for leakage inductance in the coil end.
Fig.1 shows that inductance has decreased by approximately 25% in a 2D analysis when compared to a 3D analysis. This is because a 2D analysis cannot account for leakage inductance in the coil end.
N-T Characteristics
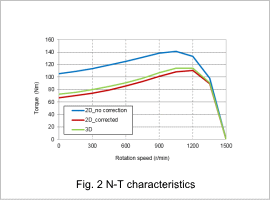
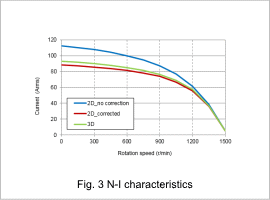
Fig.2 shows those N-T characteristics of 2D, 3D and 2D analysis with 3D correction and fig.3 shows N-I characteristics.
Fig. 2 shows that N-T characteristics becomes the same as 3D by using 3D correction. As shown in fig.3, this is because current flowing in the coil has come closer by accounting for leakage inductance.