Overview
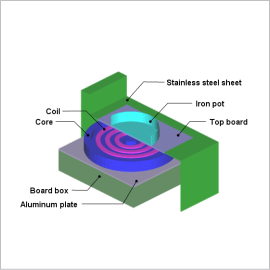
A magnetic field analysis simulation that uses the finite element method (FEM) is best for studying a three dimensional combination of the geometry, number, and alignment of the magnetic material that adjusts the magnetic circuit, and for quickly obtaining the electric circuit constant of the high frequency circuit that performs the heating.
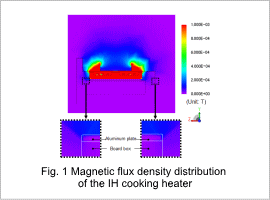
This Application Note shows how to obtain the magnetic flux density surrounding an IH cooking heater that uses high frequency induction heating and the temperature distribution of its iron pot.
Magnetic Flux Density Distribution
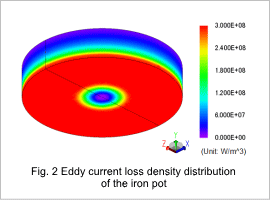
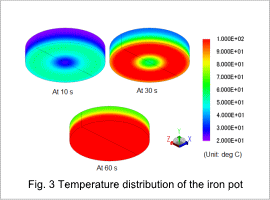
Eddy Current Loss Density Distribution and Temperature Distribution of the Iron Pot
Fig. 2 shows the eddy current loss density distribution of the iron pot. The magnetic field generated by the coil produces eddy currents on the surface of the iron pot. The iron pot is then heated because its electric resistance produces joule heat.
Fig. 3 shows the temperature distribution of the iron pot at 10 s, 30 s, and 60 s. The iron pot is heated by eddy currents. The temperature of the bottom of the iron pot rises over time, reaching 100 deg C at 60 s. In this analysis, the temperature rise of the bottom of the iron pot is not uniform. To heat the bottom of the iron pot uniformly during heating, the coil arrangement and the core geometry need to be improved.