Wireless Power Transfer
JMAG makes it possible to carry out investigations ranging from basic RLC analyses to efficiency predictions. To determine the efficiency of a wireless power transfer design, you must analyze the power transfer as a function of position and angle. This can be done quickly in JMAG using the parametric analysis tool. This tool will not only predict optimal positioning, but it will also help develop a robust and reliable design.
Evaluation Items
Self-inductance, mutual inductance, induction voltage, load current, power, copper loss, iron loss, transmission efficiency, temperature distribution
Case Studies
Power Transmission Efficiency
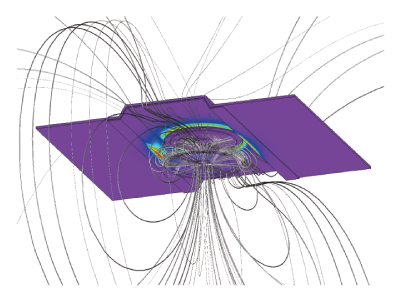
In the electromagnetic induction-type wireless power supply, magnetic flux linking to the upper power-receiving side reduces due to positional misalignment. A decrease in flux linkage causes a reduction in the mutual inductance between coils. From this the resonant frequency determined by the inductance and the capacitor is shifted, and transmission efficiency decreases. Also, when the voltage of the power-receiving side coil is constant, the input voltage on the power supply side changes, and the supply power itself reduces.